In opening a web page, the bandwidth will be used to download pages and files related, such as graphics (in various formats: GIF, JPEG, PNG, SWF), style and formatting (CSS), data (XML), and even streaming (FLV, MOV, AVI) short run automatically. The nature of the data tape utilization is sesional, or opened by the session.
For example, in the configuration of the browser (Mozilla Firefox: about: config, network.http.max-connections; about: config, network.http.max-connections-per-server) is set to a server that can only have a maximum of 8 connections, whereas total downloaded files in a web page is 32. There will be 32 sessions, with a maximum of 8 sessions running concurrently. This is a simplification (the actual principle is divided into data packets per session) to facilitate the representation that are said to be open sesional website. Examples of the characteristics of bandwidth to open a web page can be seen in Figure 1.
RealNetwork (2000) provides information on the characteristics of the streaming bandwidth utilization. Schubert et al (2008) mentions, the main challenge in doing the optimization of bandwidth for streaming purposes are to distribute streams (data streams) with high bit-rate without halting. Examples of characteristics to open stream bandwidth can be seen in Figure 1.
 Figure 1. Characteristics of the HSDPA bandwidth usage Telkomsel (maximum speed of 480 Kbps) for a single user web-session (opened with Mozilla Firefox in rotation: http://www.google.com, http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/ people/padmanab/msr-tr-2004-44.pdf, http://www.youtube.com) streaming-session (opened with Mozilla Firefox: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qZe5D3MSjOI&feature=dir ). Bandwidth utilization observed in% in speed computer-modem connection is 10 Mbps.
Figure 1. Characteristics of the HSDPA bandwidth usage Telkomsel (maximum speed of 480 Kbps) for a single user web-session (opened with Mozilla Firefox in rotation: http://www.google.com, http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/ people/padmanab/msr-tr-2004-44.pdf, http://www.youtube.com) streaming-session (opened with Mozilla Firefox: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qZe5D3MSjOI&feature=dir ). Bandwidth utilization observed in% in speed computer-modem connection is 10 Mbps.Biogeographic
1. Based on the number of Users
The use of bandwidth for multiple users in an institutional environment will be influenced by many factors: characteristics of the sites accessed, the number of users, the delay (pause) transmissions, and bandwidth available. These factors will be analyzed with the following assumptions:
1. Bandwidth optimization index is proportional to the total bandwidth available.
2. Bandwidth optimization index is inversely proportional to the number of users.
3. Bandwidth optimization index is inversely proportional to the transmission delay.
4. Bandwidth optimization index is inversely related characteristics.
From this assumption, then created the index logic optimization model of the data tape as follows:
 Description:
Description:Optimation Index = number optimization to be achieved (without units)
Bandwidth = total data bandwidth (Kbps)
User = number of users (PC connection)
Transmission delay = interval (ms delay)
Characteristic = index site characteristics (Kbps / ms delay)
2. Based on the number of requests / second
The use of bandwidth for multiple users in an institutional environment can also be approached by other factors, the number of data requests / second, not just the number of users. These factors will be analyzed with the following assumptions:
1. Bandwidth optimization index is proportional to the total bandwidth available.
2. Bandwidth optimization index is inversely proportional to the number of requests / second.
3. Bandwidth optimization index is inversely proportional to the transmission delay.
4. Bandwidth optimization index is inversely related characteristics.
From this assumption, then created the index logic optimization model of the data tape as follows:
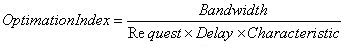 Description:
Description: Optimation Index = number optimization to be achieved (per s)
Bandwidth = total data bandwidth (Kbps)
Request = number of requests (per s)
Transmission delay = interval (ms delay)
Characteristic = index site characteristics (Kbps / ms delay)
Engineering Optimization
1. Index measures the characteristics of the site (Kbps / ms delay)
At its core is to find a minimum value for the two situations (a) a web-session (b) streaming-session is in the current conditions: minimum bandwidth, maximum delay.
2. Stress-test done at the level (amount) of a particular user
Allocate sufficient number of users. These parameters can be calculated based on the average number of users online simultaneously at peak conditions (peak load) at a measured location.
3. Stress-test done at the level of requests / second
Allocate sufficient number of requests. These parameters can be calculated based on the characteristics of users (one user opens the website and how many sessions) at a measured location.
4. Conduct stress-tests on the level of transmission delay
Getting the value of the transmission gap in peak condition at a measured location.
5. Calculating the index optimization
Optimization index is measured by equation (1) or (2). Further optimization index can be approximated by three methods: best-fit, average, minimum index.
* Best fit: index optimization, where one of the selected characteristics of bandwidth utilization priority (eg priority to open stream more than opening web page). Therefore, the results of analysis of variance (ANOVA) on the characteristics of bandwidth priority should utilitasi superior characteristics significantly from the other bandwidth utilization
* Average: index optimization explained that all the characteristics of bandwidth utilization score is not significantly different.
* The minimum index: index optimization explained that all the characteristics of bandwidth utilization in a state of minimum requirements (large data or delaynya)

No comments:
Post a Comment